Introduction
In the Sahelian zone of West Africa, mixed farming systems based on the functional integration of crops, trees/shrubs and livestock (CSL) are increasingly being considered to build resilience. But the co-design and extension of these systems poses a methodological challenge. This article presents the initial results and lessons from the mobilization of the innovation platform (IP) approach within the framework of the project "Synergistic use and protection of natural resources to strengthen rural livelihoods through the systematic integration of crops, shrubs and livestock in the Sahel". The challenge was to identify and bring together the various actors and stakeholders concerned by CSL mixed systems, both in co-design and pre-extension.
Methodology for setting up innovation platforms (IP)
The innovation platforms were set up at six sites in three countries: Yilou and Saria in Burkina Faso, Sikasso and Koulikoro in Mali, and Niakhar and Ouarkhokh in Senegal. Each site brings together several IP member villages.The participatory and inclusive approach of the Méthode Accélérée de Recherche Participative (MARP) was used to target the producer organizations that should be members of the IPs at each site.
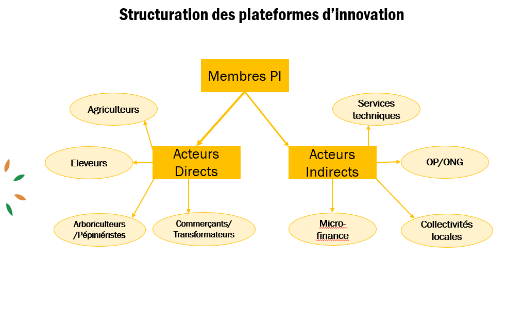
Composition of innovation platforms (IPs)
IPs are made up of an average of 20 to 25 members, including direct stakeholders (farmers, breeders, traders, arboriculturists, agricultural product processors, etc.) and indirect stakeholders (agricultural extension services, research, local authorities, microfinance, POs and NGOs, etc.).
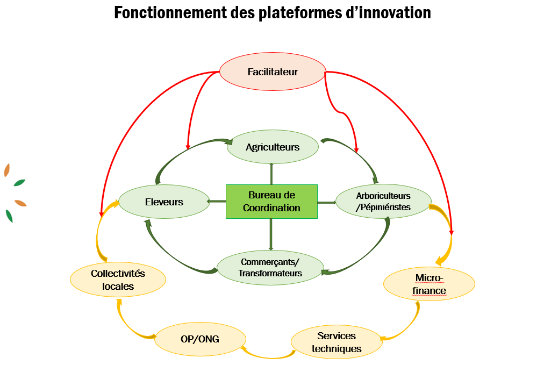
Functioning of innovation platforms
IP meetings are held quarterly and chaired by the President of the IP Management Board. Facilitation of IP meetings is managed by an indirect player, namely RESCAR-AOC for the IPs set up under the SustainSahel project.
Advantages of the co-creation of knowledge and innovations and first results of the operation of innovation platforms
Holding IP exchange meetings promoted:
- better synergy of collaboration between producers, researchers and agricultural advisory services;
- taking into account the real needs of producers, therefore directing research and extension activities on knowledge and innovations that interest producers;
- better development of local knowledge through the sharing of this knowledge between producers and between producers and technicians and especially the planning of experiments at the research level to assess the effectiveness and optimal conditions for applying certain endogenous knowledge;
- better appropriation of technologies and their adoption, which contributes to improving household food security.
Link between innovation and scaling
To facilitate the adoption of innovative technologies, a synergy has been created between the co-creation of knowledge and innovations with the adoption of this knowledge and innovations. To this end, producers, called “volunteer producers” were chosen per village to experiment with the innovations proposed by the IP. Thus, open days are organized on the research sites and these volunteer producers are invited to participate in these days. This allows them to see the technologies being tested and make choices based on their interests and the results of these technologies.
Related Links
ICARDA: Online training on innovation platforms, https://elearning.icarda.org/course/info.php?id=109&lang=fr
CORAF: Practical guide to setting up and facilitating an innovation platform, https://frao.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/Guide_CORAF_Franc%CC%A7ais_final.pdf

 tap and then scroll down to the Add to Home Screen command.
tap and then scroll down to the Add to Home Screen command.